Project Units
MENU: Simulate â Project Units...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+U
FUNCTION: Sets the geometrical units of the project
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: You can also access the Units dialog by double-clicking on the units box in the Status Bar. The default unit of a new project is millimeters. The other available options are microns, centimeters, meters, kilometers, mils, inches, feet and miles.
PYTHON COMMAND: set_units(units)
Frequency Settings
MENU: Simulate â Frequency Settings...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+F
FUNCTION: Sets the center frequency and bandwidth of the project
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: You can also access the Frequency Settings dialog by double-clicking on the frequency box in the Status Bar. The default units of frequency and bandwidth are GHz. The other available options are Hz, kHz, MHz and THz. "fc" is a reserved project variable for its center frequency and "bw" is a a reserved project variable for its bandwidth. Both fc and bw must be expressed in Hz.
PYTHON COMMAND:
set_frequency(value)
set_bandwidth(value)
Materials
MENU: Simulate â Materials...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+T
FUNCTION: Opens EM.Cube's materials list
PYTHON COMMAND: None
EM.Cube provides a preloaded database of popular and widely used materials. You can view the various material entries and their constitutive parameter values. You can also type in the first letter of a material to find it. For example, typing V selects Vacuum in the list.
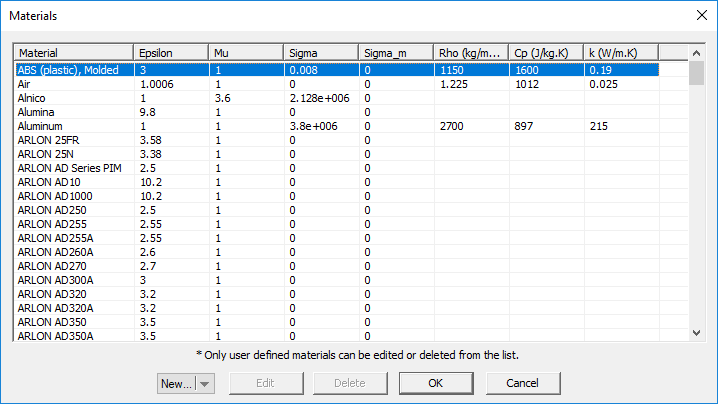 EM.Cube's Materials List. |
Domain Settings
MENU: Simulate â Computational Domain â Domain Settings...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+A
FUNCTION: Sets the type & parameters of the computational domain
PYTHON COMMAND:
set_domain_offset(dxn_offset,dxp_offset,dyn_offset,dyp_offset,dzn_offset,dzp_offset)
set_domain_offset_lambda(dxn_offset,dxp_offset,dyn_offset,dyp_offset,dzn_offset,dzp_offset)
Boundary Conditions
MENU: Simulate â Computational Domain â Boundary Conditions...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: None
FUNCTION: Sets the type of boundary conditions on the faces of the computational domain in EM.Tempo & EM.Ferma
PYTHON COMMAND: set_boundary_conditions(xn_type,xp_type,yn_type,yp_type,zn_type,zp_type)
Mesh Generator
MENU: Simulate â Discretization â Show Mesh...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+M
FUNCTION: Generates and displays the mesh of the physical structure in the current EM.Cube module
PYTHON COMMAND: mesh()
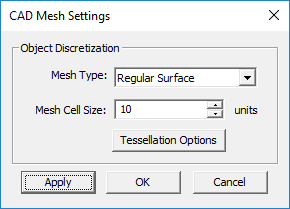
Mesh Settings
MENU: Simulate â Discretization â Mesh Settings...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+G
FUNCTION: Sets the density or resolution of the mesh and other related parameters
PYTHON COMMAND:
cubecad_mesh_settings(cell_size,angle_tol)
emtempo_mesh_settings(cells_per_lambda,ratio_contour,ratio_thin,ratio_abs)
emterrano_mesh_settings(edge_length,angle_tol)
emillumina_mesh_settings(cells_per_lambda)
emferma_mesh_settings(cell_size_x,cell_size_y,cell_size_z)
empicasso_mesh_settings(cells_per_lambda)
emlibera_mesh_settings(cells_per_lambda)
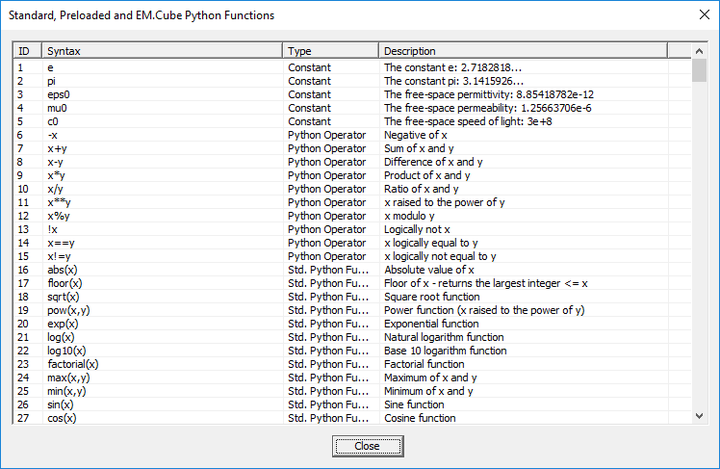
Functions
MENU: Simulate â Functions...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+I
FUNCTION: Opens the list of standard, preloaded and EM.Cube Python functions
PYTHON COMMAND: None
The table below gives a list of all the currently available library functions in EM.Cube:
| Function Name / Syntax | Description | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| sign(x) | Sign function | 1 if x>0, -1 if x<0 | |
| fac(x) | Factorial | for integer values of x: n! = n(n-1)(n-2)...3.2.1 | |
| fac2(x) | Double factorial | for even integer values of x: n!! = n(n-2)(n-4)...4.2, for odd integer values of x: n!! = n(n-2)(n-4)...5.3 | |
| ceiling(x) | Ceiling function | nearest integer >= x | |
| floor(x) | Floor function | nearest integer <= x | |
| power(x,y) | Power function | x^y or x**y | |
| sqrt(x) | Square root function | x^(1/2) or x**(1/2) | |
| exp(x) | Exponential function | e^x or e**x | |
| log10(x) | Base 10 logarithm function | ln(x)/ln(10) | |
| db(x) | Decibel function | 10*log10(x) | |
| ln(x) | Natural logarithm function | - | |
| log(x,a) | Base a logarithm function | ln(x)/ln(a) | |
| rms(x) | Root mean square function | - | |
| abs(x) | Absolute value function | x if x>0, -x if x<0 | |
| sin(x) | Sine function | - | |
| cos(x) | Cosine function | - | |
| tan(x) | Tangent function | - | |
| sec(x) | Secant function | - | |
| csc(x) | Cosecant function | - | |
| cot(x) | Cotangent function | - | |
| asin(x) | Inverse sine function | - | |
| acos(x) | Inverse cosine function | - | |
| atan(x) | Inverse tangent function | - | |
| atan2(x,y) | Inverse tangent function | - | |
| asec(x) | Inverse secant function | - | |
| acsc(x) | Inverse cosecant function | - | |
| acot(x) | Inverse cotangent function | - | |
| sinh(x) | Hyperbolic sine function | - | |
| cosh(x) | Hyperbolic cosine function | - | |
| tanh(x) | Hyperbolic tangent function | - | |
| sech(x) | Hyperbolic secant function | - | |
| csch(x) | Hyperbolic cosecant function | - | |
| coth(x) | Hyperbolic cotangent function | - | |
| asinh(x) | Inverse hyperbolic sine function | - | |
| acosh(x) | Inverse hyperbolic cosine function | - | |
| atanh(x) | Inverse hyperbolic tangent function | - | |
| asech(x) | Inverse hyperbolic secant function | - | |
| acsch(x) | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant function | - | |
| acoth(x) | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function | - | |
| Ci(x) | Cosine integral function | see Trigonometric Integral on Wikipedia. | |
| Si(x) | Sine integral function | see Trigonometric Integral on Wikipedia. | |
| C(x) | Cosine Fresnel integral function | see Fresnel Integral on Wikipedia. | |
| S(x) | Sine Fresnel integral function | see Fresnel Integral on Wikipedia. | - |
| Ellip_E(x) | Elliptic function of the first kind | see Elliptic Integral on Wikipedia. | |
| Ellip_K(x) | Elliptic function of the second kind | see Elliptic Integral on Wikipedia. | - |
| Ei(x) | Exponential integral function | see Exponential Integral on Wikipedia. | |
| En(n,x) | Generalized exponential integral function of order n | see Exponential Integral on Wikipedia. | |
| gauss(x) | Gaussian function | - | |
| erf(x) | Error function | see Error Function on Wikipedia. | |
| gamma(x) | Gamma function | see Gamma Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Airy_A(x) | Airy function of the first kind | see Airy Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Airy_B(x) | Airy function of the second kind | see Airy Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Jn(n,x) | Bessel function of the first kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Yn(n,x) | Bessel function of the second kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| In(n,x) | Modified Bessel function of the first kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Kn(n,x) | Modified Bessel function of the second kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| SB_jn(n,x) | Spherical Bessel function of the first kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| SB_yn(n,x) | Spherical Bessel function of the second kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| SB_in(n,x) | Modified spherical Bessel function of the first kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| SB_kn(n,x) | Modified spherical Bessel function of the second kind and order n | see Bessel Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Pn(n,x) | Legendre function of the first kind and order n | see Legendre Polynomial on Wikipedia. | |
| Qn(n,x) | Legendre function of the second kind and order n | see Legendre Polynomial on Wikipedia. | |
| Tn(n,x) | Chebyshev polynomial of the first kind and order n | see Chebyshev Polynomial on Wikipedia. | |
| Un(n,x) | Chebyshev polynomial of the second kind and order n | see Chebyshev Polynomials on Wikipedia. | |
| LGn(n,x) | Laguerre polynomial of order n | see Laguerre Polynomials on Wikipedia. | |
| Hn(n,x) | Hermite polynomial of order n | see Hermite Polynomials on Wikipedia. | |
| Un(n,x) | Hermite-Gauss function of order n | - | |
| Math_ce(n,r,x) | Even periodic (cosine) Mathieu function of order n | see Mathieu Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Math_se(n,r,x) | Odd periodic (sine) Mathieu function of order n | see Mathieu Function on Wikipedia. | |
| Rect(x) | Rectangle function | x|â¤0.5, 0 elsewhere | |
| Tri(x) | Triangle function | 1-x|â¤1, 0 elsewhere | |
| Spln2(x) | Quadratic spline function | - | |
| Spln3(x) | Cubic spline function | - | |
| Step(x) | Step function | 1 if x>0, 0 if x<0 | |
| Haar(x) | Haar function | x|<0.5, 0 elsewhere | |
| Ramp(x) | Ramp function | - | |
| Trapz(a,x) | Trapezoidal function | - | |
| Sqwv(x) | Square wave function | - | |
| Stwv(x) | Sawtooth wave function | - | |
| Trwv(x) | Triangle wave function | - | |
| Plstr(d,x) | Pulse train function with duty cycle d | - | |
| Sinc(d,x) | Sinc function | sin(pi*x)/(pi*x) | |
| Fejer(n,x) | Fejer function of order n | - | |
| Rand(x) | Random function | - | |
| Fltr_B(n,x) | Butterworth filter function of order n | - | |
| Fltr_CH1(n,e,x) | Chebyshev filter function of the first kind, order n | e: ripple factor e | |
| Fltr_CH2(n,e,x) | Chebyshev filter function of the second kind, order n | e: ripple factor e | |
| Fltr_E(n,s,e,x) | Elliptic filter function of order n | s: selectivity factor s, ripple factor e, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12 | |
| Z0_MS(e,x) | Characteristic impedance of a microstrip transmission line | x: width-to-height ratio, e: substrate permittivity | |
| w_MS(z,e,t) | Width of a microstrip transmission line | z: characteristic impedance, e: substrate permittivity, t: substrate thickness | |
| eeff_MS(e,x) | Effective permittivity of a microstrip transmission line | x: width-to-height ratio, e: substrate permittivity | |
| woh_MS(e,z) | Width-to-height ratio of a microstrip transmission line | z: characteristic impedance z, e: substrate permittivity | |
| Z0_CPW(e,x,y) | Characteristic impedance of a coplanar waveguide transmission line | x: slot width-to-height ratio, y: center strip width-to-height ratio, e: substrate permittivity | |
| eeff_CPW(e,x,y) | Effective permittivity of a coplanar waveguide transmission line | x: slot width-to-height ratio, y: center strip width-to-height ratio, e: substrate permittivity | |
| horn_a(d,x,y) | Wavelength-normalized a-dimension of an optimal pyramidal horn antenna | d: directivity d, x and y: wavelength-normalized waveguide dimensions | |
| horn_b(d,x,y) | Wavelength-normalized b-dimension of an optimal pyramidal horn antenna | d: directivity d, x and y: wavelength-normalized waveguide dimensions | |
| horn_l(d,x,y) | Wavelength-normalized length of an optimal pyramidal horn antenna | d: directivity d, x and y: wavelength-normalized waveguide dimensions |
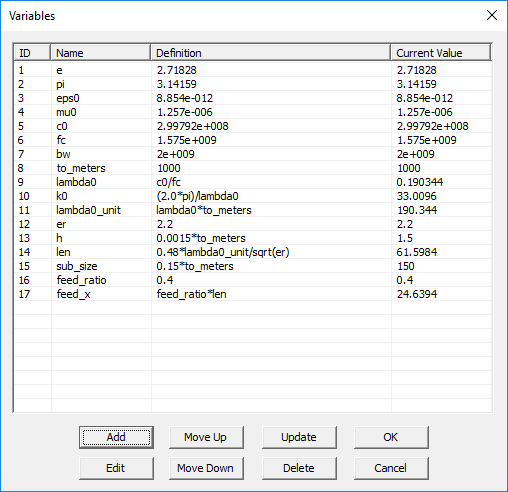
Variables
MENU: Simulate â Variables...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+B
FUNCTION: Opens the list of constants, default project variables and available user-defined variables
PYTHON COMMAND: None
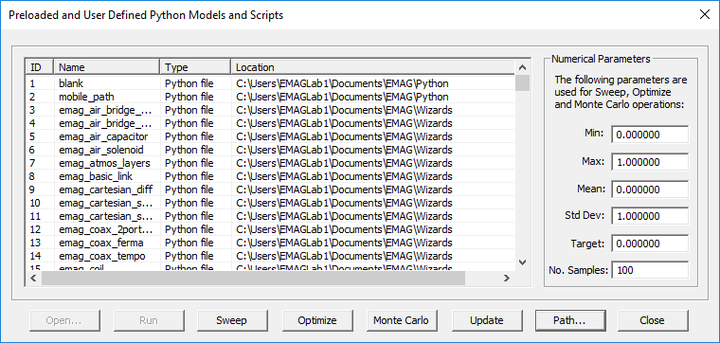
Models
MENU: Simulate â Python Models & Scripts...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+L
FUNCTION: Opens the list of the preloaded and currently available user-defined Python models and scripts
PYTHON COMMAND: None
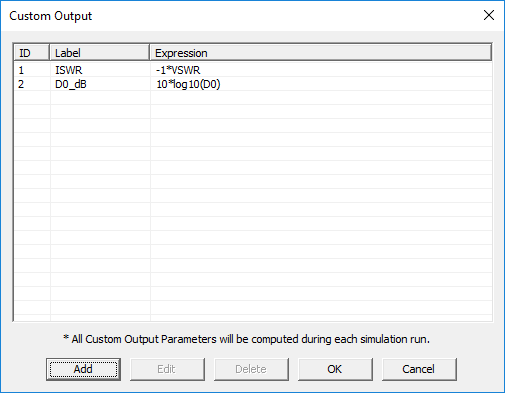
Custom Output
MENU: Simulate â Cutom Output...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+K
FUNCTION: Opens the list of the currently available user-defined custom Outputs
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Objectives
MENU: Simulate â Objective...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+J
FUNCTION: Opens the list of the currently available user-defined design objectives
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Data Manager
MENU: Simulate â Data Manager...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+D
FUNCTION: Opens EM.Cube's Data Manager
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Generate Input Files
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â Generate Input Files...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: None
FUNCTION: Generates all the necessary input files to run a simulation in one of EM.Cube's computational modules
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Simulation Engine Settings
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â Simulation Engine Settings...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+Shift+N
FUNCTION: Sets the numerical user-accessible simulation parameters in one of EM.Cube's computational modules
PYTHON COMMAND:
emtempo_engine_settings(engine,power_threshhold,max_timesteps)
emterrano_engine_settings(bounce_count,do_edge_diffraction,angular_resolution,ray_threshhold)
emillumina_engine_settings(engine,is_fixed_iteration,error_tol,max_iterations)
emferma_engine_settings(matrix_solver,error_tol,max_iterations)
empicasso_engine_settings(matrix_solver,error_tol,max_iterations)
emlibera_engine_settings_smom(matrix_solver,error_tol,max_iterations,ncpus,formulation,alpha)
emlibera_engine_settings_wmom(matrix_solver,error_tol,max_iterations)
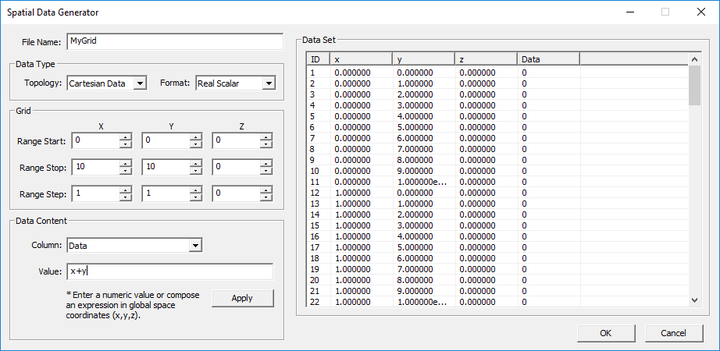
3D Data Generator
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â 3D Data Generator...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+Shift+D
FUNCTION: Opens EM.Cube's 3D Data Generator
PYTHON COMMAND: None
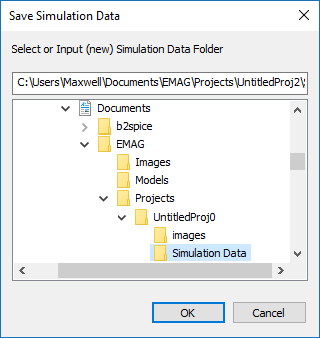
Save Data As
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â Save Data As...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: None
FUNCTION: Saves a project's data files in a specified subfolder other than the current project folder
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: This operation opens up the "Save Data" dialog with the default file path set to a subfolder named "Simulation Data" under your current project folder. You can choose the default subfolder name and location or change the name or browse to another location on your hard drive. it is important to keep in mind that before every simulation, EM.Cube deletes all the data files in the current project folder. In order to preserve your simulation data, you have to save them in a different folder other than the project folder.
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Delete All Data Files
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â Delete All Data Files
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: None
FUNCTION: Deletes all the data files in the current project folder
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Delete All Visualization Data
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â Delete All Visualization Data
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: None
FUNCTION: Deletes all the visualization data under the "Observables" section of the navigation tree
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Update All Visualization Data
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â Update All Visualization Data
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: None
FUNCTION: Reloads all the visualization data under the "Observables" section of the navigation tree from the respective 3D data files in the current project file
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: This operation is particularly useful when the simulation engine resides on another computer (e.g. on a Linux machine) and is run from the command line. At the end of the simulation, you can transfer all the output simulation data files including the 3D data files like ".RAD", ".SEN", ".CUR", "RCS", etc. to your Windows computer for data visualization.
PYTHON COMMAND: None
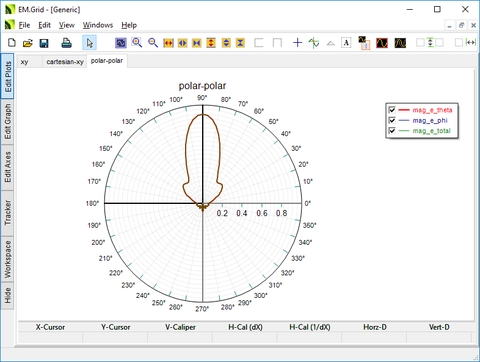
EM.Grid
ICON: None
MENU: Simulate â EM.Grid...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+Shift+G
FUNCTION: Opens EM.Grid for plotting data files
PYTHON COMMAND: plot_file(filename)
Windows Calculator
MENU: Simulate â Windows Calculator...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: None
FUNCTION: Opens Windows calculator
PYTHON COMMAND: None
Simulation Run
MENU: Simulate â Run...
KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: Ctrl+R
FUNCTION: Opens the Simulation Run dialog where you can set the simulation engine type & simulation mode and run a new simulation in one of EM.Cube's computational modules
PYTHON COMMAND: run_analysis()