Difference between revisions of "EM.Ferma"
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Domain Boundary Conditions) |
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Domain Boundary Conditions) |
||
| Line 272: | Line 272: | ||
*EM.Ferma provides two options for thermal boundary conditions on the domain box. The Dirichlet boundary condition is the default option and is specified as a fixed temperature value on the surface of the domain walls. By default, this value is 0°C. The Neumann boundary condition specifies the normal derivative of the temperature on the surface of the domain walls. This is equivalent to a constant heat flux passing through the domain walls and its value is specified in W/m<sup>2</sup>. A zero heat flux means a perfectly insulated domain box and is known as the adiabatic boundary condition. | *EM.Ferma provides two options for thermal boundary conditions on the domain box. The Dirichlet boundary condition is the default option and is specified as a fixed temperature value on the surface of the domain walls. By default, this value is 0°C. The Neumann boundary condition specifies the normal derivative of the temperature on the surface of the domain walls. This is equivalent to a constant heat flux passing through the domain walls and its value is specified in W/m<sup>2</sup>. A zero heat flux means a perfectly insulated domain box and is known as the adiabatic boundary condition. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is a one-to-one correspondence between electrostatic and thermal simulation entities: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col"| Electrostatic Item | ||
| + | ! scope="col"| Corresponding Thermal Item | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Electric Scalar Potential | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Temperature | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Electric Field | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Heat Flux Density | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Perfect Electric Conductor | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Perfect Thermal Conductor | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Dielectric Material | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Insulator Material | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Volume Charge | ||
| + | | style="width:200px;" | Volume Heat Source | ||
| + | |} | ||
To modify the boundary conditions, right-click on "Boundary Conditions" in the navigation tree, and select "Boundary Conditions..." from the contextual menu to open the Boundary Conditions Dialog. | To modify the boundary conditions, right-click on "Boundary Conditions" in the navigation tree, and select "Boundary Conditions..." from the contextual menu to open the Boundary Conditions Dialog. | ||
Revision as of 14:52, 12 June 2018
Electrostatic and Magnetostatic Solvers For DC And Low Frequency Simulations
Contents
- 1 Product Overview
- 2 EM.Ferma Features at a Glance
- 3 Building the Physical Structure in EM.Ferma
- 4 EM.Ferma's Computational Domain
- 5 EM.Ferma's Simulation Data & Observables
- 6 Discretizing the Physical Structure in EM.Ferma
- 7 Running Static Simulations in EM.Ferma
- 8 The 2D Quasi-Static Simulation Mode
Product Overview
EM.Ferma in a Nutshell
EM.Ferma is a 3D static solver. It features two distinct electrostatic and magnetostatic simulation engines and a steady-state thermal simulation engine that can be used to solve a variety of static and low-frequency electromagnetic and thermal problems. The thermal solver includes both conduction and convection heat transfer mechanisms. All the three simulation engines are based on finite difference solutions of Poisson's equation for electric and magnetic potentials and temperature.
With EM.Ferma, you can explore the electric fields due to volume charge distributions or fixed-potential perfect conductors, and magnetic fields due to wire or volume current sources and permanent magnets. Your structure may include dielectric or magnetic (permeable) material blocks. Using the thermal simulator, you can solve for the steady-state temperature distribution of structures that include perfect thermal conductors, insulators and volume heat sources. You can also use EM.Ferma's 2D quasi-static mode to compute the characteristic impedance (Z0) and effective permittivity of transmission line structures with complex cross section profiles.
![]() Click here to learn more about the Theory of Electrostatic and Magnetostatic Methods.
Click here to learn more about the Theory of Electrostatic and Magnetostatic Methods.
EM.Ferma as the Static Module of EM.Cube
EM.Ferma is the low-frequency Static Module of EM.Cube, a comprehensive, integrated, modular electromagnetic modeling environment. EM.Ferma shares the visual interface, 3D parametric CAD modeler, data visualization tools, and many more utilities and features collectively known as CubeCAD with all of EM.Cube's other computational modules.
![]() Click here to learn more about EM.Cube Modeling Environment.
Click here to learn more about EM.Cube Modeling Environment.
Advantages & Limitations of EM.Ferma's Static Simulator
EM.Ferma computes the electric and magnetic fields independent of each other based on electrostatic and magnetostatic approximations, respectively. As a result, any "electromagnetic" coupling effects or wave retardation effects are ignored in the simulation process. In exchange, static or quasi-static solutions are computationally much more efficient than the full-wave solutions of Maxwell's equations. Therefore, for low-frequency electromagnetic modeling problems or for simulation of sub-wavelength devices, EM.Ferma offers a faster alternative to EM.Cube's full-wave modules like EM.Tempo, EM.Picasso or EM.Libera. EM.Ferma currently provides a fixed-cell brick volume mesh generator. To model highly irregular geometries or curved objects, you may have to use very small cell sizes, which may lead to a large computational problem.
EM.Ferma Features at a Glance
Physical Structure Definition
- Perfect electric conductor(PEC) solids and surfaces (Electrostatics)
- Dielectric objects (Electrostatics)
- Magnetic (permeable) objects (Magnetostatics)
- Perfect thermal conductor (PTC) solids and surfaces (Thermal)
- Insulator objects (Thermal)
Sources
- Fixed-potential PEC for maintaining equi-potential metal objects (Electrostatics)
- Volume charge sources (Electrostatics)
- Volume current sources (Magnetostatics)
- Wire current sources (Magnetostatics)
- Permanent magnets (Magnetostatics)
- Fixed-temperature PTC for maintaining iso-thermal objects (Thermal)
- Volume heat sources (Thermal)
Mesh generation
- Fixed-size brick cells
3D Electrostatic & Magnetostatic Simulation
- Finite difference solution of Laplace and Poisson equations for the electric scalar potential with Dirichlet and Neumann domain boundary conditions
- Finite difference solution of Laplace and Poisson equations for the magnetic vector potential with Dirichlet domain boundary conditions
- Calculation of electric scalar potential and electric field
- Calculation of magnetic vector potential and magnetic field
- Calculation of electric flux over user defined flux boxes and capacitance
- Calculation of magnetic flux over user defined flux surfaces and inductance
- Calculation of electric and magnetic energies, Ohmic power loss and resistance
- Parametric sweep with variable object properties or source parameters
2D Quasi-Static Simulation
- 2D Finite difference solution of cross section of transmission line structures
- 3D domain solution as well as 2D solution of a longitudinally infinite version of the structure defined on a 2D plane
- Calculation of electric potential and electric field distribution
- Parametric sweep of transmission line's geometric and material parameters
- Optimization of transmission line's parameters for impedance design
Steady-State Thermal Simulation
- Finite difference solution of Laplace and Poisson equations for the temperature with Dirichlet and Neumann domain boundary conditions
- Calculation of temperature and heat flux density
- Calculation of thermal energy density on field sensor planes
- Calculation of thermal flux over user defined flux boxes
- Calculation of thermal energy
Data Generation & Visualization
- Electric and magnetic field intensity and vector plots on planes
- Electric potential intensity plots
- Animation of field and potential plots after parametric sweeps
- Graphs of characteristic impedance and effective permittivity of transmission line structures vs. sweep variables
- Custom output parameters defined as mathematical expressions of standard outputs
Building the Physical Structure in EM.Ferma
Variety of Physical Objects in EM.Ferma
The simplest static problems involve a charge source in the free space that produces an electric field, or a current source in the free space that produces a magnetic field. In such cases, the only applicable boundary conditions are defined at the boundary of the computational domain. As soon as you introduce a dielectric object next to a charge source or a magnetic (permeable) material next to a current source, you have to deal with a complex boundary value problem. In other words, you need to solve the electric or magnetic Poisson equation subject to the domain boundary conditions as well as material interface boundary conditions. The simplest thermal problem involves one or more thermal plates held at fixed temperatures. Once you introduce material blocks, you have to enforce conductive and convective boundary conditions at the interface between different materials and air. EM.Ferma uses the Finite Difference (FD) technique to find a numerical solution of your static boundary value problem.
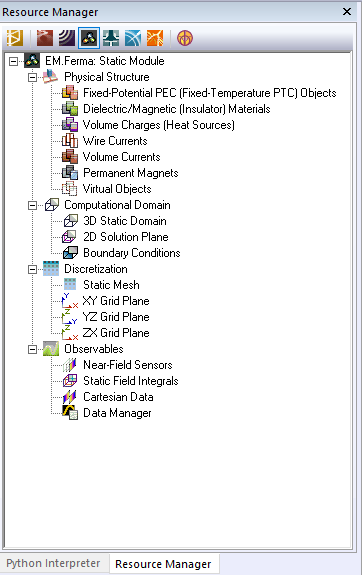
EM.Ferma offers the following types of physical objects:
| Icon | Physical Object Type | Applications | Geometric Object Types Allowed | Notes & Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Fixed-Potential Perfect Electric Conductor (PEC) | Modeling perfect metals with a fixed voltage | Solid and surface objects | Can be considered an electric source if the fixed voltage is nonzero |
| |
Dielectric/Magnetic Material | Modeling any homogeneous or inhomogeneous material | Solid objects | non-source material |
| |
Volume Charge | Modeling volume charge sources with a fixed charge density or an expression in the global coordinates (x,y,z) | Solid objects | Acts as an electric source |
| |
Volume Current | Modeling volume current sources with a fixed volume current density vector or expressions in the global coordinates (x,y,z) | Solid objects | Acts as a magnetic source |
| |
Permanent Magnet | Modeling permanent magnet sources with a fixed magnetization vector or expressions in the global coordinates (x,y,z) | Solid objects | Acts as a magnetic source |
| |
Wire Current | Modeling wire current sources | line and polyline objects | Acts as a magnetic source |
| |
Fixed-Temperature Perfect Thermal Conductor (PTC) | Modeling iso-thermal surfaces with a fixed temperature | Solid and surface objects | Can be considered a thermal source if the fixed temperature is different than the ambient temperature (shares the same navigation tree node as PEC object) |
| |
Insulator Material | Modeling any homogeneous or inhomogeneous material | Solid objects | non-source material (shares the same navigation tree node as dielectric material) |
| |
Volume Heat Source | Modeling volume heat sources with a fixed heat density or an expression in the global coordinates (x,y,z) | Solid objects | Acts as a thermal source (shares the same navigation tree node as volume charge) |
Click on each category to learn more details about it in the Glossary of EM.Cube's Materials, Sources, Devices & Other Physical Object Types.
Grouping Objects by Material or Source Type
Your physical structure in EM.Ferma is typically made up of some kind of source object either in the free space or in the presence of one or more material objects. EM.Ferma's electrostatic and magnetostatic or thermal simulation engines then discretize the entire computational domain including these source and material objects and solve the Laplace or Poisson equations to find the electric or magnetic fields or temperature everywhere in the computational domain.
All the geometric objects in the project workspace are organized together into object groups which share the same properties including color and electric or magnetic parameters. It is recommended that you first create object groups, and then draw new objects under the active group. To create a new object group, right-click on its category name in the "Physical Structure" section of the navigation tree and select one of the "Insert New Group..." items from the contextual menu. However, if you start a new EM.Ferma project from scratch, and start drawing a new object without having previously defined any object groups, a new default "Fixed-Potential PEC" object group with a zero voltage is created and added to the navigation tree to hold your new geometric object.
Once a new object group node has been created in the navigation tree, it becomes and remains the "Active" object group, which is always listed in bold letters. When you draw a new geometric object such as a box or a sphere, its name is added under the currently active object group. There is only one object group that is active at any time. Any group can be made active by right-clicking on its name in the navigation tree and selecting the Activate item of the contextual menu.
![]() Click here to learn more about Moving Objects among Different Groups.
Click here to learn more about Moving Objects among Different Groups.
A Note on Material and Source Types in EM.Ferma
In EM.Cube's other modules, material types are categorized under the "Physical Structure" section of the navigation tree, and sources are organized under a separate "Sources" section. In those modules, all the geometric objects you draw in your project workspace typically represent material bodies. All of EM.Cube modules except for EM.Ferma require at least one excitation source to be selected from the "Sources" section of the navigation tree before you can run a simulation.
In EM.Ferma, materials and sources are all lumped together and listed under the "Physical Structure" section of the navigation tree. In other words, there is no separate "Sources" section. For example, you can define default zero-potential perfect electric conductors (PEC) in your project to model metal objects. You can also define fixed-potential PEC objects with a nonzero voltage, which can effectively act as a voltage source for your boundary value problem. In this case, you will solve the Lapalce equation subject to the specified nonzero potential boundary values. Both types of PEC objects are defined from the same PEC node of the navigation tree by assigning different voltage values. Charge and current sources are also defined as geometric objects, and you have to draw them in the project workspace just like other material objects.
EM.Ferma's Computational Domain
The Domain Box
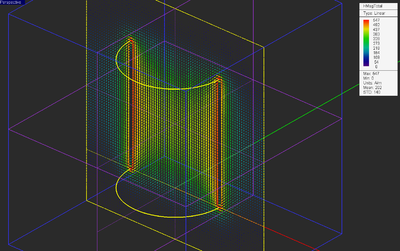
In EM.Ferma, the Poisson or Laplace equations are solved subject to boundary conditions using the Finite Difference technique. As a result, you need to specify a finite computational domain and then specify the domain boundary conditions. EM.Ferma's computational domain defines where the domain boundary condition will be specified. A default domain box is always placed in the project workspace as soon as you draw your first object. The domain can be seen as a blue cubic wireframe that surrounds all of the CAD objects in the project workspace.
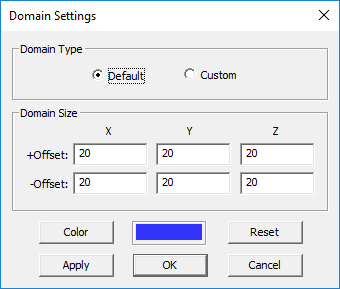
To modify the domain settings, click the Domain button of the Simulate Toolbar or right-click on "3D Static Domain" entry in the Navigation Tree and select "Domain Settings..." from the contextual menu. In the Domain Settings Dialog, the computational domain can be defined in two different ways: Default and Custom. The default type places an enclosing box with a specified offset from the largest bounding box of your project's CAD objects. The default offset value is 20 project units, but you can change this value arbitrarily. The custom type defines a fixed domain box by specifying the coordinates of its two opposite corners labeled Min and Max in the world coordinate system.
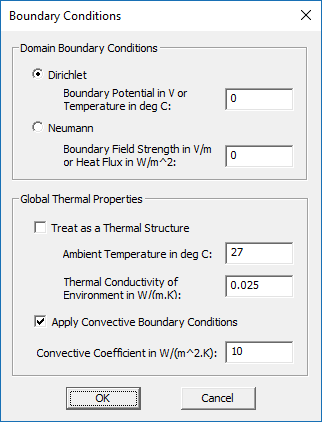
Domain Boundary Conditions
- EM.Ferma allows you to specify the electric potential boundary conditions on the domain box. Two options are available. The Dirichlet boundary condition is the default option and is specified as a fixed potential value on the surface of the domain walls. By default, this value is 0 Volts. The Neumann boundary condition specifies the normal derivative of the electric scalar potential on the surface of the domain walls. This is equivalent to a constant normal electric field component on the domain walls and its value is specified in V/m.
- The magnetostatic simulation engine always assumes Dirichlet domain boundary conditions and sets the values of the magnetic vector potential to zero on all the domain walls.
- EM.Ferma provides two options for thermal boundary conditions on the domain box. The Dirichlet boundary condition is the default option and is specified as a fixed temperature value on the surface of the domain walls. By default, this value is 0°C. The Neumann boundary condition specifies the normal derivative of the temperature on the surface of the domain walls. This is equivalent to a constant heat flux passing through the domain walls and its value is specified in W/m2. A zero heat flux means a perfectly insulated domain box and is known as the adiabatic boundary condition.
There is a one-to-one correspondence between electrostatic and thermal simulation entities:
| Electrostatic Item | Corresponding Thermal Item |
|---|---|
| Electric Scalar Potential | Temperature |
| Electric Field | Heat Flux Density |
| Perfect Electric Conductor | Perfect Thermal Conductor |
| Dielectric Material | Insulator Material |
| Volume Charge | Volume Heat Source |
To modify the boundary conditions, right-click on "Boundary Conditions" in the navigation tree, and select "Boundary Conditions..." from the contextual menu to open the Boundary Conditions Dialog.
| |
You can switch between the electrostatic and thermal solvers from the boundary conditions dialog. |
EM.Ferma's Simulation Data & Observables
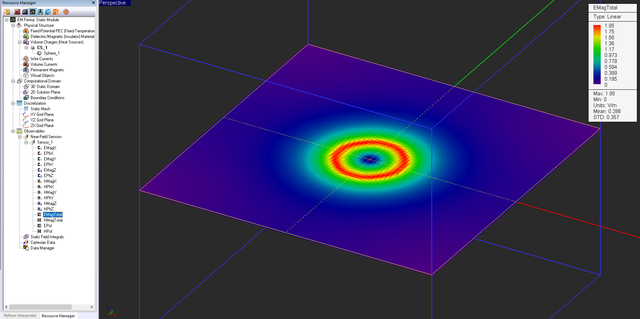
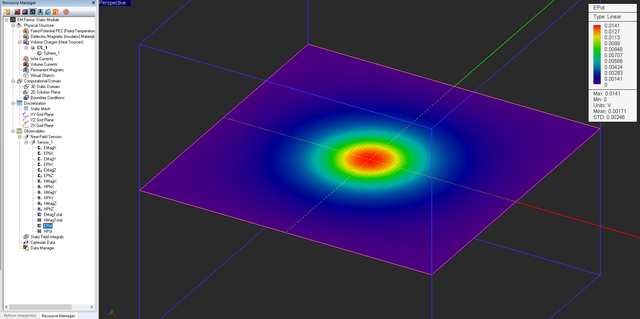
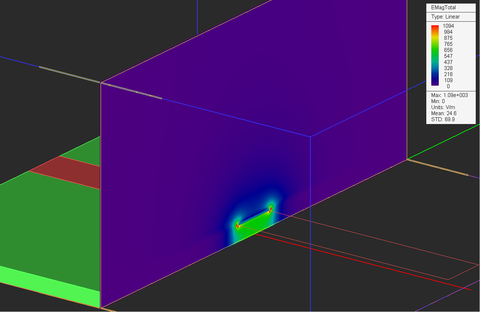
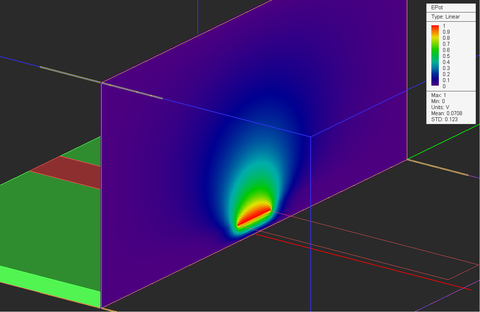
At the end of an electrostatic simulation, the electric field vector and electric scalar potential values are computed at all the mesh grid points of the entire computational domain. At the end of an magnetostatic simulation, the magnetic field vector and magnetic vector potential values are computed at all the grid nodes. Besides the electric and magnetic fields, EM.Ferma can compute a number of field integral quantities such as voltage, current, flux, energy, etc. The field components, potential values and field integrals are written into output data files and can be visualized on the screen or graphed in EM.Grid only if you define a field sensor or a field integral observable. In the absence of any observable defined in the navigation tree, the static simulation will be carried out and completed, but no output simulation data will be generated.
EM.Ferma offers the following types of output simulation data:
| Icon | Simulation Data Type | Observable Type | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| |
Near-Field Distribution Maps | Near-Field Sensor | Computing electric and magnetic field components, electri scalar potential and magnitude of magnetic vector potential on a planar cross section of the computational domain |
| |
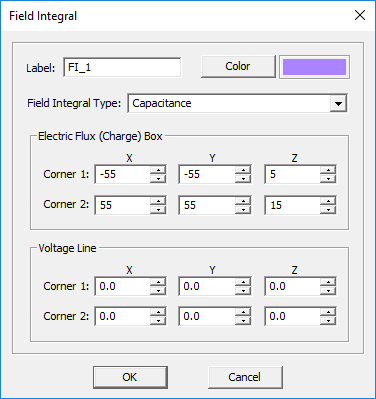
Field Integral Quantities | Static Field Integral | Computing line, surface and volume integrals of the electric and magnetic fields and heat flux |
Click on each category to learn more details about it in the Glossary of EM.Cube's Simulation Observables & Graph Types.
The table below list the different types of field integrals and their definitions:
| Field Integral | Definition | Output Data File |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | [math] V = - \int_C \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{dl} [/math] | voltage.DAT |
| Current | [math] I = \oint_{C_o} \mathbf{H(r)} . \mathbf{dl} [/math] | current.DAT |
| Conduction Current | [math] I_{cond} = \int\int_S \mathbf{J(r)} . \mathbf{ds} = \int\int_S \sigma \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{ds} [/math] | conduction_current.DAT |
| Electric Flux | [math] \Phi_E = \int\int_{S_o} \mathbf{D(r)} . \mathbf{ds} = \int\int_{S_o} \epsilon \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{ds} [/math] | flux_E.DAT |
| Magnetic Flux | [math] \Phi_H = \int\int_S \mathbf{B(r)} . \mathbf{ds} = \int\int_S \mu \mathbf{H(r)} . \mathbf{ds} [/math] | flux_H.DAT |
| Electric Energy | [math] W_E = \frac{1}{2} \int \int \int_V \epsilon \vert \mathbf{E(r)} \vert ^2 dv [/math] | energy_E.DAT |
| Magnetic Energy | [math] W_H = \frac{1}{2} \int\int\int_V \mu \vert \mathbf{H(r)} \vert ^2 dv [/math] | energy_H.DAT |
| Ohmic Power Loss | [math] P_{ohmic} = \int\int\int_V \sigma \vert \mathbf{E(r)} \vert ^2 dv [/math] | ohmic.DAT |
| Capacitance | [math] C = \Phi_E/V = \int\int_{S_o} \epsilon \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{ds} / \int_C \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{dl} [/math] | capacitance.DAT |
| Capacitance (Alternative) | [math] C = 2W_E/V^2 = 2 \int \int \int_V \epsilon \vert \mathbf{E(r)} \vert ^2 dv / \left( \int_C \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{dl} \right)^2[/math] | capacitance.DAT |
| Self-Inductance | [math] L = \Phi_H/I = \int\int_S \mu \mathbf{H(r)} . \mathbf{ds} / \oint_{C_o} \mathbf{H(r)} . \mathbf{dl} [/math] | inductance.DAT |
| Self-Inductance (Alternative) | [math] L = 2W_M/I^2 = 2 \int \int \int_V \mu \vert \mathbf{H(r)} \vert ^2 dv / \left( \oint_{C_o} \mathbf{H(r)} . \mathbf{dl} \right)^2[/math] | inductance.DAT |
| Mutual Inductance | [math] M = \Phi_H^{\prime}/I = \int\int_{S^{\prime}} \mu \mathbf{H(r)} . \mathbf{ds} / \oint_{C_o} \mathbf{H(r)} . \mathbf{dl} [/math] | mutual_inductance.DAT |
| Resistance | [math] R = V/I_{cond} = - \int_C \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{dl} / \int\int_S \sigma \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{ds} [/math] | resistance.DAT |
| Resistance (Alternative 1) | [math] R = V^2/P_{ohmic} = \left( \int_C \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{dl} \right)^2 / \int\int\int_V \sigma \vert \mathbf{E(r)} \vert ^2 dv [/math] | resistance.DAT |
| Resistance (Alternative 2) | [math] R = P_{ohmic}/I_{cond}^2 = \int\int\int_V \sigma \vert \mathbf{E(r)} \vert ^2 dv / \left( \int\int_S \sigma \mathbf{E(r)} . \mathbf{ds} \right)^2[/math] | resistance.DAT |
| Thermal Flux | [math] \Phi_T = \int\int_{S_o} \mathbf{q(r)} . \mathbf{ds} [/math] | flux_T.DAT |
| Thermal Energy | [math] W_T = Q = \int \int \int_V \rho_V c_p \left( T\mathbf{(r)} - T_{env} \right) dv [/math] | energy_T.DAT |
Discretizing the Physical Structure in EM.Ferma
The Static Mesh
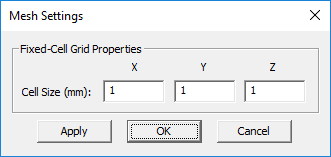
The Finite Difference technique discretizes the computational domain using a 3D rectangular grid. EM.Ferma generates a fixed-cell mesh. This means that the extents of the mesh cells along the principal axes are fixed: Δx, Δy, Δz. By default, the mesh cell size is set to one unit project along all the three directions (with Δx = Δy = Δz). To modify the cell size, click the Mesh Settings button of the Simulate Toolbar or right-click on "Static Mesh" in the Navigation Tree, and select "Mesh Settings..." from the contextual menu to open the Mesh Settings Dialog.
| |
To obtain accurate results, it is highly recommended to use a square mesh as much as possible. |
![]() Click here to learn more about Working with Mesh Generator.
Click here to learn more about Working with Mesh Generator.
![]() Click here to learn more about the properties of EM.Ferma's Fixed-Cell Brick Mesh Generator.
Click here to learn more about the properties of EM.Ferma's Fixed-Cell Brick Mesh Generator.
Running Static Simulations in EM.Ferma
EM.Ferma's Simulation Modes
EM.Ferma currently offers three different simulation modes as follows:
| Simulation Mode | Usage | Number of Engine Runs | Frequency | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analysis | Simulates the physical structure "As Is" | Single run | N/A | None |
| Parametric Sweep | Varies the value(s) of one or more project variables | Multiple runs | N/A | None |
| Optimization | Optimizes the value(s) of one or more project variables to achieve a design goal | Multiple runs | N/A | None |
Running an Electrostatic or Magnetostatic Analysis
EM.Ferma has two independent but functionally similar static simulation engines: Electrostatic and Magnetostatic. The electrostatic engine solves the electric form of Poisson's equation for electric scalar potential subject to electric field boundary conditions, in the presence of electric sources (volume charges and fixed-potential PEC blocks) and dielectric material media. The magnetostatic engine solves the magnetic form of Poisson's equation for magnetic vector potential subject to magnetic field boundary conditions, in the presence of magnetic sources (wire and volume currents and permanent magnetic blocks) and magnetic material media.
In EM.Ferma you don't have to select any specific simulation engine. The program looks at the types sources and material objects present in your project workspace and then it determines whether an electrostatic analysis or a magnetostatic analysis or possibly both should be performed. When there are only electric sources present, you will get nonzero electric fields and zero magnetic fields. When there are only magnetic sources present, you will get nonzero magnetic fields and zero electric fields.
An "Analysis" is the simplest simulation mode of EM.Ferma. It is a single-shot finite difference solution of your static problem. The physical structure of your project workspace is first discretized using a fixed-cell mesh and the Poisson equation is solved numerically everywhere in the computational domain. The field and potential values at each mesh node are computed, and the specified observables are written into data files.
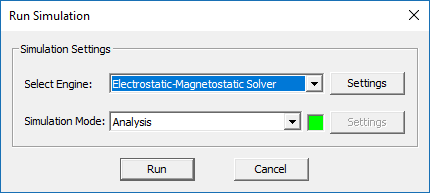
To run a static simulation, first you have to open the Run Dialog. This is done by clicking the "Run" button of the Simulate Toolbar, or by selecting the "Run" item of the Simulate Menu, or simply using the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl+R". The only available simulation engine is "Static". Clicking the Run button of this dialog starts a static analysis. A separate window pops up which reports the progress of the current simulation.
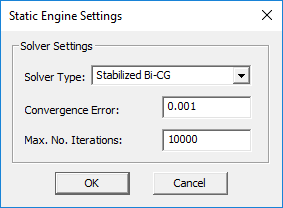
Static Simulation Engine Settings
EM.Ferma currently uses a single iterative linear system solver based on the stabilized Bi-Conjugate Gradient (BiCG) method to solve the matrix equations which result from the discretization of Poisson's equation. You can specify some numerical parameters related to the Bi-CG solver. To do that, you need to open the Simulation Engine Settings Dialog by clicking the "Settings" button located next to the "Select Engine" drop-down list. From this dialog you can set the maximum number of BiCG iterations, which has a default value of 10,000. You can also set a value for "Convergence Error". The default value for electrostatic analysis is 0.001. For magnetostatic analysis, the specified value of convergence error is reduced by a factor 1000 automatically. Therefore, the default convergence error in this case is 1e-6.
The 2D Quasi-Static Simulation Mode
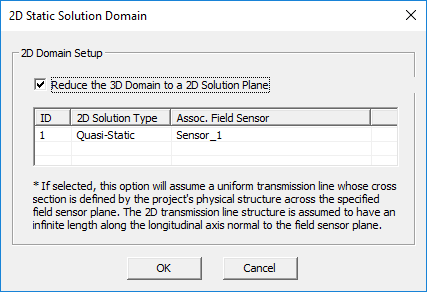
EM.Ferma's electrostatic simulation engine features a 2D solution mode where your physical model is treated as a longitudinally infinite structure in the direction normal to specified "2D Solution Plane". A 2D solution plane is defined based on a "Field Sensor" definition that already exists in your project. To explore EM.Ferma's 2D mode, right-click on 2D Solution Planes in the "Computational Domain" section of the navigation tree and select 2D Domain Settings... from the contextual menu. In the 2D Static Domain dialog, check the checkbox labeled "Reduce the 3D Domain to a 2D Solution Plane". The first field sensor observable in the navigation tree is used for the definition of the 2D solution plane.
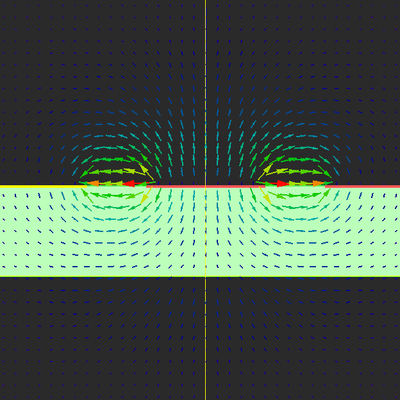
At the end of a 2D electrostatic analysis, you can view the electric field and potential results on the field sensor plane. It is assumed that your structure is invariant along the direction normal to the 2D solution plane. Therefore, your computed field and potential profiles must be valid at all the planes perpendicular to the specified longitudinal direction.
You can also use EM.Ferma to perform a quasi-static analysis of multi-conductor transmission line structures, which usually provides good results at lower microwave frequencies (f < 10GHz).
EM.Ferma computes the characteristics impedance Z0 and effective permittivity εeff of your TEM or quasi-TEM transmission line. The results are written to two output data files named "solution_plane_Z0.DAT" and "solution_plane_EpsEff.DAT", respectively.
![]() Click here to learn more about the theory of 2D Quasi-Static Analysis of Transmission Lines.
Click here to learn more about the theory of 2D Quasi-Static Analysis of Transmission Lines.