Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with EM.Cube"
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→EM.Cube's Modular Architecture) |
(→EM.Cube's Modular Architecture) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[EM.Cube]] brings together several computational modules that can be used to solve a large variety of electromagnetic modeling and RF design problems. Each module revolves around a specific numerical method that is optimized for a certain class of problems or applications. [[EM.Cube]]'s framework is based on total separation of the visual software interface and simulation engines. The numerical solvers communicate with the [[EM.Cube]] application solely through ASCII input and output files. This makes it possible to utilize the same user interface effectively to drive different simulation engines. | [[EM.Cube]] brings together several computational modules that can be used to solve a large variety of electromagnetic modeling and RF design problems. Each module revolves around a specific numerical method that is optimized for a certain class of problems or applications. [[EM.Cube]]'s framework is based on total separation of the visual software interface and simulation engines. The numerical solvers communicate with the [[EM.Cube]] application solely through ASCII input and output files. This makes it possible to utilize the same user interface effectively to drive different simulation engines. | ||
| − | At the heart of [[EM.Cube]] is [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]], a general-purpose parametric CAD modeling environment. [[EM.Cube]]'s computational modules are all customized variations of [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]] equipped with a particular simulation engine. Therefore, they all share the same input utilities (geometry definition and mesh generation) and same output utilities (data visualization and processing). [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]] features a powerful 3D CAD modeler with a large selection of native objects (solids, surfaces, curves) and a wide range of object creation, editing and transformation tools. You can import external CAD files with different popular standard formats. [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]]'s intuitive, mouse-driven, point-and- | + | At the heart of [[EM.Cube]] is [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]], a general-purpose parametric CAD modeling environment. [[EM.Cube]]'s computational modules are all customized variations of [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]] equipped with a particular simulation engine. Therefore, they all share the same input utilities (geometry definition and mesh generation) and same output utilities (data visualization and processing). [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]] features a powerful 3D CAD modeler with a large selection of native objects (solids, surfaces, curves) and a wide range of object creation, editing and transformation tools. You can import external CAD files with different popular standard formats. [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]]'s intuitive, mouse-driven, point-and-click and drag-and-drop tools let you quickly build very sophisticated structures either from the ground up or by combining native objects with imported external structures. You can also export your projects to a number of popular CAD formats. [[EM.Cube]]'s Data Manager is a versatile utility for processing and plotting your simulation data either as 3D visualizations overlaid on your physical structure or in the form of a variety of graph types. |
In addition to [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]], [[EM.Cube]] currently offers six distinct computational modules: | In addition to [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]], [[EM.Cube]] currently offers six distinct computational modules: | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
Static Module </td> | Static Module </td> | ||
<td style="border-color: rgb(153, 153, 204); padding: 10px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"> | <td style="border-color: rgb(153, 153, 204); padding: 10px; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"> | ||
| − | This module features | + | This module features three electrostatic, magnetostatic and steady-state thermal simulation engines that can be used for static or low-frequency analysis of circuits, lumped devices and transmission lines. </td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | Besides sharing a common CAD modeler and common data visualization tools, all computational modules | + | Besides sharing a common CAD modeler and common data visualization tools, all computational modules follow a common structure with similar features and attributes as follows: |
*Physical Structure | *Physical Structure | ||
*Computational Domain | *Computational Domain | ||
| + | *Discretization | ||
*Sources | *Sources | ||
*Observables | *Observables | ||
| − | |||
| − | The specific contents of each | + | The above attributes are what you normally need to define and specify before you run a computer simulation of a physical problem. First, you have to define the physical structure to be analyzed within a well-defined computational domain. The physical structure and possibly the computational domain need to be discretized using some kind of mesh generator. Next, you have to define a source for exciting your physical structure. Finally, you need to specify appropriate simulation observables to generate data that characterize the behavior of your physical structure. Now you can run the simulation engine, i.e., one of [[EM.Cube]]'s several electromagnetic solvers. |
| + | |||
| + | The specific contents of each attribute may vary from module to module depending on the underlying physics. For example, the geometric objects listed under your project's physical structure have different sets of properties in each module. Some source types like plane waves and Hertzian short dipoles or some observable types like field sensors, far-field radiation patterns and radar cross section (RCS) have identical definitions in all computational modules. Of [[EM.Cube]]'s computational modules, [[EM.Tempo]] serves as a general-purpose electromagnetic simulator that can handle most types of modeling problems involving arbitrary geometries and complex material variations in both time and frequency domains. | ||
== EM.Cube Installation == | == EM.Cube Installation == | ||
| Line 121: | Line 123: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Operating System | ! scope="row"| Operating System | ||
| + | | Windows 10 | ||
| Windows 8.1 or higher | | Windows 8.1 or higher | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Processor | ! scope="row"| Processor | ||
| − | | Intel | + | | i9 Intel |
| − | | Intel | + | | i7 or i5 Intel |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| RAM | ! scope="row"| RAM | ||
| − | | | + | | 32GB |
| − | | | + | | 8GB |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Graphics Card | ! scope="row"| Graphics Card | ||
| − | | | + | | 8GB NVIDIA RTX |
| − | | | + | | 4GB NVIDIA Quadro |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Display | ! scope="row"| Display | ||
| + | | Ultra HD | ||
| HD (1080p) 96 DPI | | HD (1080p) 96 DPI | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 156: | Line 158: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope"row" rowspan="2"| Other Platforms | ! scope"row" rowspan="2"| Other Platforms | ||
| − | | | + | | Firefox 3.0 or later with Javascript and Cookies enabled. |
|- | |- | ||
| Flash Plugin 8.0 or later. | | Flash Plugin 8.0 or later. | ||
| Line 246: | Line 248: | ||
* '''Wizard Toolbar''': This toolbar provides easy access to most of [[EM.Cube]]'s preloaded wizards. | * '''Wizard Toolbar''': This toolbar provides easy access to most of [[EM.Cube]]'s preloaded wizards. | ||
* '''Simulate Toolbar''': This toolbar provides access to most important simulation-related functions and operation such as the mesh generator and the simulation run dialog. | * '''Simulate Toolbar''': This toolbar provides access to most important simulation-related functions and operation such as the mesh generator and the simulation run dialog. | ||
| − | |||
<table> | <table> | ||
| Line 276: | Line 277: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| − | [[Image:Modulebar_new.png|thumb|left| | + | [[Image:Modulebar_new.png|thumb|left|450px|The module bar and navigation tree allow you to move among [[EM.Cube]]'s modules and access the properties of the current project's various items in each module.]] |
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 283: | Line 284: | ||
=== Navigation Tree === | === Navigation Tree === | ||
| − | The Navigation Tree provides all the details of an entire [[EM.Cube]] project. These include the CAD objects and geometric models, material assignments, computational domain and boundary conditions, mesh | + | The Navigation Tree provides all the details of an entire [[EM.Cube]] project. These include the CAD objects and geometric models, material assignments, computational domain and boundary conditions, mesh parameters, source information, observable definitions, etc. Besides the menu bar and toolbars, the navigation tree serves as another place from which you can modify most items in your project. Similar to the toolbars, you can undock, move around or hide the module bar and navigation tree. |
The contents of the navigation tree vary depending on the selected module. In [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]], the navigation tree features two main sections: Geometrical Construction and Data Visualization. The "Geometrical Construction" section holds your geometric objects, while the "Data Visualization" section is used for generation of 3D data visualizations to be displayed in the project workspace. In other modules, the navigation tree typically features five distinct sections: | The contents of the navigation tree vary depending on the selected module. In [[Building_Geometrical_Constructions_in_CubeCAD | CubeCAD]], the navigation tree features two main sections: Geometrical Construction and Data Visualization. The "Geometrical Construction" section holds your geometric objects, while the "Data Visualization" section is used for generation of 3D data visualizations to be displayed in the project workspace. In other modules, the navigation tree typically features five distinct sections: | ||
| Line 315: | Line 316: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| − | [[Image:Newproj1.png|thumb|left| | + | [[Image:Newproj1.png|thumb|left|800px|EM.Cube's New Project dialog.]] |
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:55, 7 March 2021
Visual Electromagnetic Modeling Environment for Simulating Everything from DC to Light
Contents
An EM.Cube Primer
EM.Cube in a Nutshell
EM.Cube is a visual software environment for electromagnetic (EM) modeling. It features several distinct simulation engines that can solve a wide range of modeling problems such as electromagnetic radiation, scattering, wave propagation in various media, coupling, interference, signal integrity, field interactions with biological systems, etc. Using EM.Cube, you can solve problems of different sizes and length scales, varying from a few microns in MEMS devices to several miles in large urban propagation scenes.
EM.Cube has a highly integrated modular architecture. Its six computational modules offer a mix of full-wave, static and asymptotic numerical solvers in both time and frequency domains. An intuitive, streamlined user interface is shared among all of EM.Cube's computational modules and simulation engines. Once you learn the basics of the software application, you will find enormous computational power at your fingertips. EM.Cube allows you to plan and execute complex, system-level simulations of multi-scale electromagnetic structures.
![]() Click here to learn more about Examples of EM.Cube's Applications.
Click here to learn more about Examples of EM.Cube's Applications.
EM.Cube's Modular Architecture
EM.Cube brings together several computational modules that can be used to solve a large variety of electromagnetic modeling and RF design problems. Each module revolves around a specific numerical method that is optimized for a certain class of problems or applications. EM.Cube's framework is based on total separation of the visual software interface and simulation engines. The numerical solvers communicate with the EM.Cube application solely through ASCII input and output files. This makes it possible to utilize the same user interface effectively to drive different simulation engines.
At the heart of EM.Cube is CubeCAD, a general-purpose parametric CAD modeling environment. EM.Cube's computational modules are all customized variations of CubeCAD equipped with a particular simulation engine. Therefore, they all share the same input utilities (geometry definition and mesh generation) and same output utilities (data visualization and processing). CubeCAD features a powerful 3D CAD modeler with a large selection of native objects (solids, surfaces, curves) and a wide range of object creation, editing and transformation tools. You can import external CAD files with different popular standard formats. CubeCAD's intuitive, mouse-driven, point-and-click and drag-and-drop tools let you quickly build very sophisticated structures either from the ground up or by combining native objects with imported external structures. You can also export your projects to a number of popular CAD formats. EM.Cube's Data Manager is a versatile utility for processing and plotting your simulation data either as 3D visualizations overlaid on your physical structure or in the form of a variety of graph types.
In addition to CubeCAD, EM.Cube currently offers six distinct computational modules:
|
|
CubeCAD | CAD Module | This is the basic 3D CAD modeling environment for creation, import and export of native and external geometric objects. |
|
|
EM.Tempo | FDTD Module | This module features an FDTD simulator for full-wave time domain modeling of 3D objects, circuits, antennas, complex materials and periodic structures. |
|
|
EM.Terrano | Propagation Module | This module features an asymptotic SBR ray tracer for physics-based, site specific modeling of radio wave propagation in urban and natural environments. |
|
|
EM.Ferma | Static Module | This module features three electrostatic, magnetostatic and steady-state thermal simulation engines that can be used for static or low-frequency analysis of circuits, lumped devices and transmission lines. |
|
|
EM.Picasso | Planar Module | This module features a 2.5-D Method of Moments (MoM) solver for full-wave frequency domain modeling of multilayer printed antennas, microwave circuits and periodic planar structures. |
|
|
EM.Libera | MoM3D Module | This module features two 3D Method of Moments (MoM) solvers for full-wave frequency domain modeling of 3D free-space structures: A Wire MoM simulator and a Surface MoM simulator. |
|
|
EM.Illumina | Physical Optics Module | This module features an iterative Physical Optics (PO) solver for asymptotic modeling of electromagnetic scattering from large metallic structures and impedance surfaces in the free space. |
Besides sharing a common CAD modeler and common data visualization tools, all computational modules follow a common structure with similar features and attributes as follows:
- Physical Structure
- Computational Domain
- Discretization
- Sources
- Observables
The above attributes are what you normally need to define and specify before you run a computer simulation of a physical problem. First, you have to define the physical structure to be analyzed within a well-defined computational domain. The physical structure and possibly the computational domain need to be discretized using some kind of mesh generator. Next, you have to define a source for exciting your physical structure. Finally, you need to specify appropriate simulation observables to generate data that characterize the behavior of your physical structure. Now you can run the simulation engine, i.e., one of EM.Cube's several electromagnetic solvers.
The specific contents of each attribute may vary from module to module depending on the underlying physics. For example, the geometric objects listed under your project's physical structure have different sets of properties in each module. Some source types like plane waves and Hertzian short dipoles or some observable types like field sensors, far-field radiation patterns and radar cross section (RCS) have identical definitions in all computational modules. Of EM.Cube's computational modules, EM.Tempo serves as a general-purpose electromagnetic simulator that can handle most types of modeling problems involving arbitrary geometries and complex material variations in both time and frequency domains.
EM.Cube Installation
The EM.Cube application has been built on a Microsoft Windows platform. While the main program requires a Windows operating system to run, its simulation engines are platform-independent and can be run on Linux platforms or high performance computing (HPC) clusters. If you intend to run one or more of EM.Cube’s simulation engines on a platform other than Microsoft Windows, please contact our technical support for more information and guidance.
Hardware Requirements
| RECOMMENDED | MINIMUM | |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows 10 | Windows 8.1 or higher |
| Processor | i9 Intel | i7 or i5 Intel |
| RAM | 32GB | 8GB |
| Graphics Card | 8GB NVIDIA RTX | 4GB NVIDIA Quadro |
| Display | Ultra HD | HD (1080p) 96 DPI |
If you have any questions regarding the ability of your system to run EM.Cube, please contact our technical support.
Browser Requirements
| BROWSER | |
|---|---|
| Windows | Google Chrome, Internet Explorer 8.0 or later with Javascript and Cookies enabled. |
| Flash Active X plugin 8.0 or later. | |
| Other Platforms | Firefox 3.0 or later with Javascript and Cookies enabled. |
| Flash Plugin 8.0 or later. |
Running the Installer
- Double click on the installer to begin installing the EM.Cube software.
- Read and accept the license agreement.
- Follow the prompts until the installation process is completed.
| |
You must be an Administrator on your computer to run the installer. If you are using Windows 7, right click the installer and choose "Run as Administrator." |
Placing the EM.Cube License File
EM.Cube Pro requires a valid license to run on any machine. Once you install EM.Cube on a computer and launch it for the first time, the screen displays a unique EM-ID key, which is made up of a sequence of numbers and letters. You need to write down the EM-ID key and email it to us. We will generate a license file based on the EM-ID key and will email it to you. You need to place the license file that has a ".lic" file extension in the directory "C:/Program Files (x86)/EMAG/Licenses/".
Getting to Know EM.Cube's Visual Interface
Before you start using EM.Cube, it is important to familiarize yourself with its visual user interface. This is called the EM.Cube Desktop and consists of a number of visual elements:
- Splash Screen
- Main Window at the center of the screen
- Menu Bar at the top of the screen
- Six horizontal and vertical toolbars scattered at the top, left and right of the screen
- Wide Control Window on the left of the screen with two tabs: Navigation Tree and Python Interpreter
- Status Bar at the bottom of the screen
- Quick Tips on the right of the screen
 The visual elements of the EM.Cube Desktop. |
Splash Screen
The splash screen pops up every time you launch the application. It has four buttons:
- New: Lets you start a brand-new project.
- Open: Lets you open an existing project.
- Help: Opens your browser and takes you the the EM.Cube Wiki.
- Update: Checks for new updates and alerts you if your EM.Cube version is no the latest one.
You can click one of the four buttons of the splash screen to proceed. Or you can simply close it using either its "x" button at the upper right corner or using the keyboard's Esc button.
Main Window
The main window with a default dark background occupies the largest part of the EM.Cube desktop. The main window is also referred to as the Project Workspace throughout the EM.Cube documentation. This is where most of your interaction with EM.Cube such as CAD construction and data visualization takes place. All the input to EM.Cube's simulation engines is created and assembled through the main window, including geometrical and material definitions, sources, boundary conditions, meshes, and observables, i.e. the output quantities you instruct EM.Cube to generate at the end of a simulation. After a simulation run is completed, the main window is where you view the 3D visualization of the simulation results.
Menu Bar
EM.Cube's standard menus are:
- File Menu: This menu allows you to manage (create, open, save and close) EM.Cube projects. It also provides the ability to import external CAD files or export CAD files into formats that can be used by other software packages. Printing is accessed from the File Menu.
- Edit Menu: This menu provides Undo, Redo, Cut, Copy, Paste, and Delete – all of which can be used to manage your CAD objects. Through the Preferences dialog, you can set a number of global settings for the EM.Cube application including color preferences, etc.
- View Menu: The menu lets you hide or show the navigation tree, status bar, and various shortcut toolbars. View Menu also allows you to pan, rotate, and zoom in and out of the current view of the main window. You can change EM.Cube's several snap modes from this menu. You can also change the viewing angle of the main window to a variety of pre-selected viewpoints (front, back, perspective, etc.) You can access the Split Viewports option, which splits the main window into a four-port view. You can change the current work plane from View Menu and toggle the grid from the default adaptive type to a fixed custom grid.
- Object Menu: This menu provides one of the several methods for creating geometric objects including solids, surfaces, curves and points.
- Tools Menu: This menu allows you to access all the object editing and transformation tools as well as EM.Cube's wizards
- Simulate Menu: This menu contains all the settings, tools and utilities that drive EM.Cube's computational modules. From this menu you get access to project units and frequency settings, computational domain, mesh generator, variables, models, custom output, objectives, data manager and simulation Run dialog.
- Help Menu: This menu reports the current version of EM.Cube, displays the current EM-ID and provides a list of all the keyboard shortcuts. From this menu you can access EM.Cube's comprehensive documentation including the online manuals and tutorials for all the modules.
Toolbars
The toolbars can be used in place of the pull-down menus to perform the most commonly used functions with fewer mouse clicks. These functions are grouped into six toolbars:
- System Toolbar: This toolbar is used for general project operations as well as general edit functions.
- View Toolbar: This toolbar provides buttons for most widely used view operation such as zooming and work planes.
- Object Toolbar: This toolbar contains all the tools for drawing CubeCAD's native geoemtric object types.
- Tools Toolbar: This toolbar provides a large number of geometric object editing and transformation tools.
- Wizard Toolbar: This toolbar provides easy access to most of EM.Cube's preloaded wizards.
- Simulate Toolbar: This toolbar provides access to most important simulation-related functions and operation such as the mesh generator and the simulation run dialog.
All the toolbars can be repositioned however you like. Simply grab a toolbar's handle to undock and drag it to any location on the main window. Once undocked, you can also resize a toolbar and make it horizontal or vertical. Move the cursor to the border of the toolbar to turn it into a double arrow. Then drag the mouse until the toolbar gets the right size and appearance. You can dock an undocked toolbar by dragging and dropping it onto the border of the main window. You can show or hide any EM.Cube toolbar from Menu → View → Toolbars.
Module Bar
When you start the EM.Cube application, it lands you first in CubeCAD by default. The Module Bar located on the left edge of the screen is used to switch among CubeCAD and EM.Cube's various computational modules. It consists of eight buttons:
- CubeCAD: EM.Cube's 3D CAD modeling environment
- EM.Tempo: EM.Cube's FDTD module
- EM.Terrano: EM.Cube's propagation module
- EM.Illumina: EM.Cube's physical optics module
- EM.Ferma: EM.Cube's static module
- EM.Picasso: EM.Cube's planar module
- EM.Libera: EM.Cube's 3D MoM module
- RF.Spice A/D: This is a separate stand-alone application that can be used together with EM.Cube
Clicking on each of the first seven buttons of module bar changes the view to the selected module. Clicking on the RF.Spice A/D button, opens the RF.Spice A/D application if you have a valid license of that application.
 The module bar and navigation tree allow you to move among EM.Cube's modules and access the properties of the current project's various items in each module. |
The Navigation Tree provides all the details of an entire EM.Cube project. These include the CAD objects and geometric models, material assignments, computational domain and boundary conditions, mesh parameters, source information, observable definitions, etc. Besides the menu bar and toolbars, the navigation tree serves as another place from which you can modify most items in your project. Similar to the toolbars, you can undock, move around or hide the module bar and navigation tree.
The contents of the navigation tree vary depending on the selected module. In CubeCAD, the navigation tree features two main sections: Geometrical Construction and Data Visualization. The "Geometrical Construction" section holds your geometric objects, while the "Data Visualization" section is used for generation of 3D data visualizations to be displayed in the project workspace. In other modules, the navigation tree typically features five distinct sections:
- Physical Structure
- Computational Domain
- Discretization
- Sources
- Observables
Status Bar
Underneath the main window and at the bottom of the EM.Cube desktop, the Status Bar is located. Status Bar displays important information about the current EM.Cube project including the project unit, frequency, the current coordinate system and state of Snap to Grid and Object Snap modes. Probably the most widely used piece of information on the Status Bar is the current mouse position in the project workspace.
Python Command Window
On the right of the screen you see the Python command window. There is a Python Command Line at the bottom of this window. This is where you enter your Python commands on line at a time. After entering your command and pressing the keyboard's Enter, the command is executed and is reflected in the larger top part of the window, which maintains a history of your commands during a project session.
Managing EM.Cube Projects
Starting a New Project
When you start the EM.Cube application, the splash screen pops up. This screen walks you through the process of setting up a new project if you click its New button. Alternatively, you can close the splash screen without clicking any of its four buttons and land on a blank project workspace in CubeCAD. Here you can start drawing your new geometric objects and build a physical structure for your project.
If you click the New button of the splash screen, the New Project dialog opens up. You can also open the new project dialog at any time by selecting the menu item File → New Project..., or clicking the New ![]() button of the System Toolbar. The default name of the new project is "UntitledProj" followed by an index. The new project folder by default is created in the "Projects Folder" of your EM.Cube installation folder. This is normally located in the "EMAG Folder" inside your hard drive's "Documents Folder". From the new project dialog, you can change the location of the new project folder to anywhere on your hard drive using Windows Explorer's folder tree. Before you start the new project, you can change its name to anything you like. Simply type in a new name to replace the default "UntitledProj...".
button of the System Toolbar. The default name of the new project is "UntitledProj" followed by an index. The new project folder by default is created in the "Projects Folder" of your EM.Cube installation folder. This is normally located in the "EMAG Folder" inside your hard drive's "Documents Folder". From the new project dialog, you can change the location of the new project folder to anywhere on your hard drive using Windows Explorer's folder tree. Before you start the new project, you can change its name to anything you like. Simply type in a new name to replace the default "UntitledProj...".
The problem type is assumed to be "Generic" by default. This creates a blank project in CubeCAD by default. From CubeCAD, you can switch to any of EM.Cube's other computational modules and continue to build your project. The new project dialog lets you set the project length units. The default option is Millimeters. For computational modules, you need to set the operational frequency. The dialog lets you select the frequency unit, which is GHz (Gigahertz) by default. You can set the project's center frequency and bandwidth. Once you have changed all the settings, click the Create button to make the changes effective and start your new project. Keep in mind that you can always change the center frequency and bandwidth of your project later. However, changing the length units in the middle of a project is highly discouraged after you have already constructed a detailed physical structure.
Choosing a Problem Type
In most cases, you will prefer to start a generic or blank project and build up your physical structure either in CubeCAD or in one of EM.Cube's computational modules. EM.Cube, however, also provides a library of 16 ready-made project templates to get you started as quickly as possible. These projects cover different problem types or applications such as wave propagation, radiation, scattering, circuits, periodic structures, etc. They construct highly parameterized structures in various computational modules. Some of the benefits of the new project templates are:
- You learn how to define variables and parameterzie geometric objects, material groups and other project properties.
- You learn how to define excitation sources and simulation observables in different computational modules.
- You can use a project template as a starting point and then change various parameters or add new geometric objects or other project attributes.
- Each project template has a Python script, which you can access from the models dialog.
- You can learn how to put together simple Python scripts.
- You can use the Python scripts of the existing project templates as a starting point and create more complicated projects scenarios. You can build a library of reusable project templates.
The following table lists EM.Cube's new project templates and their purpose:
| Problem Type | Module | Python Script | Notes | Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Generic | CubeCAD | N/A | Creates a blank project. | 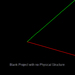
|
| 2 | Simple Outdoor Propagation Scene | EM.Terrano | emag_prop_scene.py | Creates a two brick buildings with a vertical half-wave dipole transmitter and a grid of isotropic receivers. | 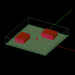
|
| 3 | Simple Indoor Propagation Scene | EM.Terrano | emag_indoor_scene.py | Creates a brick building with internal wall partitions, a vertical half-wave dipole transmitter and a grid of isotropic receivers. | 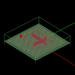
|
| 4 | General Radiation | EM.Tempo | emag_gen_radiation.py | Creates a wire dipole with a lumped source attached to a square PEC ground plane. | 
|
| 5 | General Scattering | EM.Tempo | emag_gen_scattering.py | Creates a metallic cylinder target with a dielectric coating illuminated by a vertically incident plane wave source. | 
|
| 6 | General Periodic Structure | EM.Tempo | emag_gen_periodic.py | Creates a periodic unit cell containing a metallic cross illuminated by a vertically incident plane wave source. | 
|
| 7 | General Waveguide Structure | EM.Tempo | emag_gen_waveguide.py | Creates a vertical rectangular hollow waveguide terminated in a rectangular metallic flange excited using a waveguide port. | 
|
| 8 | Finite-Sized Planar Structure | EM.Tempo | emag_finite_planar.py | Creates a probe-fed square patch on a finite-sized conductor-backed dielectric substrate excited by a lumped source on the vertical probe line. | 
|
| 9 | Planar Filter | EM.Tempo | emag_lp_filter.py | Creates a microstrip lowpass filter excited using two microstrip ports with a Gaussian pulse waveform. | 
|
| 10 | Shielded Resonator | EM.Tempo | emag_shielded_structure.py | Creates a hemispherical dielectric resonator fed through an extended cylindrical probe in a dielectric substrate at the bottom of a shielded metallic box. | 
|
| 11 | MMIC Circuit | EM.Tempo | emag_mmic.py | Creates a two-port planar component excited using two microstrip ports on a multilayer substrate inside a shielded metallic box. | 
|
| 12 | Netlist Amplifier Circuit | EM.Tempo | emag_netlist_amp.py | Creates a linear amplifier circuit containing an active two-port device with a simple Netlist model excited by two microstrip ports. | 
|
| 13 | Unbounded Planar Structure | EM.Picasso | emag_unbounded_planar.py | Creates a probe-fed square patch on a laterally unbounded conductor-backed dielectric substrate excited by a probe gap source. | 
|
| 14 | Unbounded Microstrip Structure | EM.Picasso | emag_unbounded_microstrip.py | Creates a two-port planar microstrip bandpass filter structure excited using two scattering wave ports. | 
|
| 15 | Unbounded Slot Structure | EM.Picasso | emag_unbounded_slot.py | Creates a slot structure in an unbounded ground plane excited using an underpassing micrsotrip feed with a shorting pin. | 
|
| 16 | Multilayer Periodic Surface | EM.Picasso | emag_netlist_amp.py | Creates a periodic unit cell using a concentric square loop and patch elements printed on a multilayer dielectric substrate illuminated using a plane wave source. | 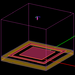
|
| 17 | Wire Structure | EM.Libera | emag_wire_structure.py | Creates a multi-wire metal structure including a spiral helix excited by a wire gap source. | 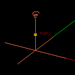
|
| 18 | Air-Filled Capacitor | EM.Ferma | emag_air_capacitor.py | Creates an air-filled parallel plate capacitor with the top plate connected to a voltage source. | 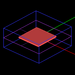
|
| 19 | Air-Core Solenoid | EM.Ferma | emag_air_solenoid.py | Creates a current-carrying vertical solenoid with an air core. | 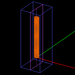
|
Opening, Saving & Closing Projects
Previously saved projects can be opened using the menu item File → Open Project..., or by clicking the Open ![]() button of the System Toolbar. If you are in a different project that has been modified, and your changes have not been saved yet, a warning message will appear asking you whether you want to save the current project before opening another project. Once the standard Windows open dialog pops up, you can browse the Windows Explorer and locate any project you wish to open. You have to open the project folder and select the project file with a ".PRJ" file extension.
button of the System Toolbar. If you are in a different project that has been modified, and your changes have not been saved yet, a warning message will appear asking you whether you want to save the current project before opening another project. Once the standard Windows open dialog pops up, you can browse the Windows Explorer and locate any project you wish to open. You have to open the project folder and select the project file with a ".PRJ" file extension.
You can save the current project using the menu item File → Save Project, or by clicking the Save ![]() button of the System Toolbar. You can save the project under another name using the menu item Menu → File → Save Project As.... This opens up the standard Windows Save Dialog. The Windows Explorer shows the current location of the project folder. You can type in any name in the provided file path. Or you may change the folder and save the project in another location. "Save As" can be used to make additional copies of the same project under different names.
button of the System Toolbar. You can save the project under another name using the menu item Menu → File → Save Project As.... This opens up the standard Windows Save Dialog. The Windows Explorer shows the current location of the project folder. You can type in any name in the provided file path. Or you may change the folder and save the project in another location. "Save As" can be used to make additional copies of the same project under different names.
You can close a project at any time using the menu item File → Close Project. A message pops up that prompts if you wish to save the existing project. You can quit the EM.Cube application using the menu item File → Quit or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Q. Note that when you close a project, you are still in the EM.Cube application. If you start a new project, you may still carry some of the program settings from the previous project. Quitting and exiting the application ensures that all the default settings would take effect the next time when you start a new project.
![]() To find additional details about EM.Cube's file operations, see the Glossary of EM.Cube's Basic File, Edit & View Operations.
To find additional details about EM.Cube's file operations, see the Glossary of EM.Cube's Basic File, Edit & View Operations.
Changing Project Settings
You can change the project length units and frequency settings at any time after you create a new project. This can be done from the Units and Frequency dialogs. The units dialog can be accessed from Menu → Simulate → Project Units or by clicking the Units ![]() button of the Simulate Toolbar. You can also open the units dialog by double-clicking the "Units" section of the status bar, which by default displays "mm".
button of the Simulate Toolbar. You can also open the units dialog by double-clicking the "Units" section of the status bar, which by default displays "mm".
The frequency dialog can be accessed from Menu → Simulate → Frequency Settings..., or by clicking the Frequency ![]() button of the simulate toolbar. The project's current center frequency is displayed on the status bar with the current frequency units. Double-clicking on this value is another way to open up the frequency dialog. From this dialog you can change the values of center frequency and bandwidth as well as the frequency units.
button of the simulate toolbar. The project's current center frequency is displayed on the status bar with the current frequency units. Double-clicking on this value is another way to open up the frequency dialog. From this dialog you can change the values of center frequency and bandwidth as well as the frequency units.
![]() To find additional details about these dialogs, see the Glossary of EM.Cube's Simulation-Related Operations.
To find additional details about these dialogs, see the Glossary of EM.Cube's Simulation-Related Operations.
Handling Project and Data Files
All the information about each EM.Cube project are stored in two files which bear the name of the project and have file extensions ".PRJ" (project file) and ".MDL" (model file). When you run a new simulation, a large number of files of different types are created in the project folder. Some of the output data files have reserved names and are overwritten after each simulation. EM.Cube deletes most of the files in the project folder before every simulation. The exceptions are the project and model files. It is very important to remember that the project folder is not a place to save your data. Every time you run a simulation, EM.Cube prompts that you are about to discard all previous results and asks whether you want to proceed.
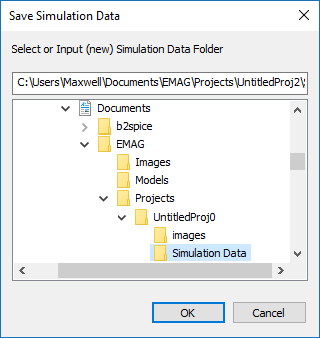
You can clean up your project folder at any time through Menu → Simulate → Delete All Data Files or by right-clicking on the Data Manager item in the "Observables" section of the navigation tree and selecting Delete All Data Files from the contextual menu. In order to preserve your simulation data, you have to save them in a different folder other than the project folder. One way is to create a subfolder in your project folder. The contents of subfolders are not deleted at the start of a simulation. To save the data in a project subfolder, select the menu item Simulate → Save Data As... or right-click on the Data Manager item in the "Observables" section of the navigation tree and select Save Data As... from the contextual menu. This opens up the Save Data dialog with the default subfolder name "Simulation Data" in your current project folder. You can choose the default subfolder name and location or change the name or browse to another location on your hard drive.
Changing EM.Cube's Visual Settings
Customizing Your Desktop
Most of the visual elements of EM.Cube's user interface can be customized. EM.Cube will remember the last state of your visual interface when you exit the application and will restore it the next time you start the application. These information are saved in the Windows registry and remain there until you delete them. You can move the menu bar and the six toolbars around and drop them at any location on the screen. Hover your mouse on the handle of any toolbar and simply drag it. The toolbars become horizontal when they are placed inside the main window. In this case, they are said to be floating inside the main window. If you hover the mouse on one of the four edges of a floating toolbar, its shape changes to a double arrow. You can expand or shrink a floating toolbar horizontally or vertically. When you drop a floating toolbar to an edge of the screen, the toolbar docks onto that edge.
You can customize the EM.Cube Desktop to your liking in a number of ways. For example, you can change its view mode temporarily, change the background color of your project workspace, and display or hide the grid. These functions can be accessed either through the "View Menu" or "View Toolbar" or through the "Preferences Dialog" of the Edit Menu, which can opened using the menu item Edit → Preferences.... In general, the changes you make through the menus and toolbars are valid during the session of your project, while the changes you make in the preferences dialog are permanent and are written to the Windows registry. That means your changes persist the next time you open the EM.Cube application.
Using a number of menu items at the top of the "View Menu", you can turn all the individual toolbars on or off, and show or hide the navigation tree and status bar. Furthermore, you can drag the handle of the navigation tree, Python command window or any of the toolbars and drop them anywhere within the project workspace.
The Grid
EM.Cube's grid is used as a guide for drawing objects. When you start the EM.Cube applciation, the grid is off by default. However, the Snap to Grid mode is enabled by default. As you move the mouse in the project workspace, a small white square follows the mouse cursor snapping to the nearest grid node. EM.Cube's grid can be turned on or off from the Guides tab of the preferences dialog. In this tab of the dialog, check the box labeled Show Grid Lines and click the Apply button of the dialog to display the grid. From this dialog you can also change the color of grid lines. You can show or hide the axis lines in the project workspace.
When the "Snap to Grid" mode is enabled, a text reading like Grid Snap: 5 appears on EM.Cube's status bar. This shows the current grid cell size. As you zoom in or zoom out, the grid cell size changes accordingly. You can turn the "Snap to Grid" mode on and off from the status bar by double-clicking on this text to toggle its state. Besides the adaptive grid that is the default grid type, EM.Cube also offers a fixed grid option, which can be zoomed in or out together with the physical structure in the project workspace.
![]() To learn more about EM.Cube's grid types, see EM.Cube's Grid Properties.
To learn more about EM.Cube's grid types, see EM.Cube's Grid Properties.
Changing the Environment Colors
The default background color of the main window is black, but it can easily be changed from the preferences dialog. Select the Colors tab of the dialog and click the button labeled Color next to Background. A color selection window pops up, where you can pick a new background color. Another global color in EM.Cube is the selection color. When you select an object, its color turns to the selection color. When you hover your mouse on an object without clicking (called the mouse-over state), it becomes translucent with a shade of the selection color. You can snap to the characteristic points of objects (e.g. vertices, edge midpoints, face centers, etc.). These snap points appear in the complementary color of the selection color. By default, EM.Cube's selection color is bright yellow, which can also be changed from the Colors tab of the preferences dialog.
Basic View Operations
When you start EM.Cube, the default grid cell size is set to 5 units. The default view may not be good enough for very small or very large structures. You can easily change the view settings of the project workspace. The simplest view operation is zooming in or out. This can easily be done using the scroll wheel of your mouse. Turning the scroll wheel towards yourself zooms out of a structure, while turning it away from yourself zooms in to the structure. Zooming in and out using the mouse scroll wheel is a temporary operation and does not change the view mode. EM.Cube provides a number of view modes, which persist until you change the mode or return to the Normal Mode. You can always return to the normal mode using the Esc (Escape) key of your keyboard. You can also return to the normal mode by clicking the Select ![]() button of the View Toolbar or selecting the menu item View → Normal View.
button of the View Toolbar or selecting the menu item View → Normal View.
The following table summarizes EM.Cube's most useful and widely used view operations. "RMB" stands for the right mouse button.
For most of EM.Cube's functions, the keyboard shortcuts simply serve as an alternative to a toolbar button or a menu item. In the case of Pan View, Rotate View and Dynamic Zoom, the RMB shortcuts provide temporary functions, while the toolbar buttons or menu item create a persistent view mode. For example, in the rotate view mode, dragging the mouse with the left or right mouse buttons held down results on the rotation of the project workspace's view about different axes of revolution. Once enabled, the rotate view mode stays active until you return to the normal view mode.
![]() To find additional details about EM.Cube's view operations, see the Glossary of EM.Cube's Basic File, Edit & View Operations.
To find additional details about EM.Cube's view operations, see the Glossary of EM.Cube's Basic File, Edit & View Operations.